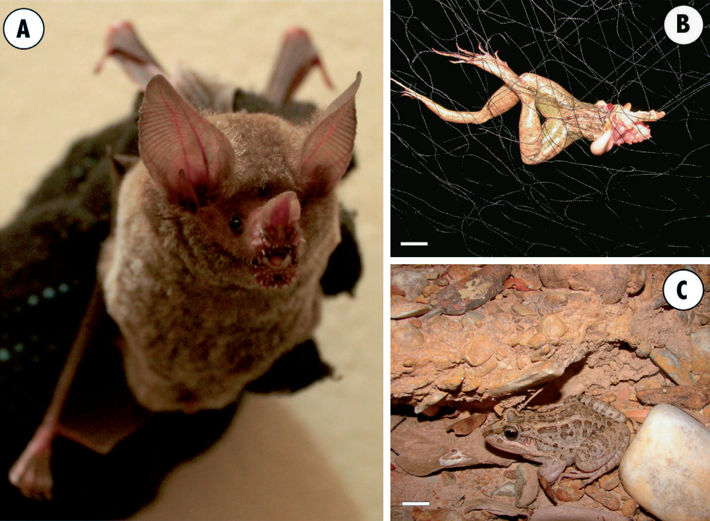
Predation of Leptodactylus macrosternum (Anura: Leptodactylidae) by the Fringe-lipped bat, Trachops cirrhosus (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae) in southeastern Brazil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31687/saremNMS.20.0.21Resumo
Embora o morcego Trachops cirhrosus seja conhecido por se alimentar de anuros, a maioria das informações sobre seus hábitos alimentares é resultado da análise de conteúdo estomacal, restos encontrados em abrigos ou alimentação experimental em cativeiro, com poucos casos observados diretamente na natureza. Neste trabalho nós reportamos T. cirrhosus predando a rã Leptodactylus macrosternum, sendo o primeiro registro deste morcego se alimentando de anuros no sudeste do Brasil, e também a primeira observação direta de um evento de predação por T. cirrhosus na natureza para esta região, contribuindo, desta forma, para o entendimento das suas relações tróficas.
Referências
Baker, R. J., S. Solari, A. Cirranelo, & N. B. Simmons. 2016. Higher level classification of Phyllostomid bats with a summary of DNA synapomorphies. Acta Chiropterologica 18:1–38.
Bonato, V., & K. G. Facure. 2000. Bat predation by the fringe-lipped bat Trachops cirrhosus (Phyllostomidae, Chiroptera). Mammalia 64:241–243.
Bonato, V., K. G. Facure, & W. Uieda. 2004. Food habits of bats of subfamily Vampyrinae in Brazil. Journal of Mammalogy 85:708–713.
Castro, I. J., & C. E. Costa-Campos. 2017. New record of anuran predation by Trachops cirrhosus (Mammalia, Chiroptera, Phyllostomidae) in a varzea forest in the estuary of the Amazon River, Eastern Amazon. Biota Amazônia 7:108–109.
Cramer, M. J., M. R. Willig, & C. Jones. 2001. Trachops cirrhosus. Mammalian Species 656:1–6.
Duellman, W. E., & Trueb, L. 1994. Biology of Amphibians. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore/London.
Leal, E. S. B., et al. 2018. What constitutes the menu of Trachops cirrhosus (Chiroptera)? A review of the species' diet. Neotropical Biology and Conservation 13:337–346.
Miller, B., F. Reid, J. Arroyo-Cabrales, A. D. Cuarón, & P. C. de Grammont. 2015. Trachops cirrhosus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015:e.T22029A22042903. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T22029A22042903.en.
Peracchi, A. L., S. T. E Albuquerque, & S. D. L. Raimundo. 1982. Contribuição ao conhecimento dos hábitos alimentares de Trachops cirrhosus (Spix, 1823) (Mammalia, Chiroptera, Phyllostomidae). Arquivos da Universidade Federal Rural do Rio de Janeiro 5:1–5.
Rocha, R., I. Silva, A. M. dos Reis, & G. M. Rosa. 2012. Another frog on the menu: predation of Trachops cirrhosus (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae) upon Osteocephalus oophagus (Anura: Hylidae). Chiroptera Neotropical 18:1136–1138.
Rocha, R., M. Gordo, & A. López-Baucells. 2016. Completing the menu: Addition of Scinax cruentommus and Scinax cf. garbei (Anura: Hylidae) to the diet of Trachops cirrhosus (Chiroptera: Phyllostomidae) in Central Amazon. North-Western Journal of Zoology 12:199–204.
Rodrigues, F. H. G., M. L. Reis, & V. S. Braz. 2004. Food habits of the Frog-eating Bat, Trachops cirrhosus, in Atlantic Forest of northeastern Brazil. Chiroptera Neotropical 10:180–182.
Ryan, M. J., & M. D. Tuttle. 1983. The ability of the Frog-eating bat to discriminate among novel and potentially poisonous frog species using acoustic cues. Animal Behaviour 31:827–833.
Silva, L. A. M., 2007. Comunidades de morcegos em uma área de Caatinga e Brejo de Altitude no agreste de Pernambuco. Brasília, DF. Tese de Doutorado. Universidade de Brasília, Brazil.
Williams, S. L., & H. H. Genoways. 2007. Subfamily Phyllostominae Gray, 1825. Mammals of South America, Volume I: Marsupials, Xenarthrans, Shrews, and Bats (A. L. Gardner, ed.). The University of Chicago Press, Chicago and London.
Zina, J., & C. F. B Haddad. 2005. Reproductive activity and vocalizations of Leptodactylus labyrinthicus (Anura: Leptodactylidae) in Southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 5:1–11.

Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2020 Fred V. de Oliveira, Rodolfo Stumpp, Maria Clara Nascimento-Costa

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.