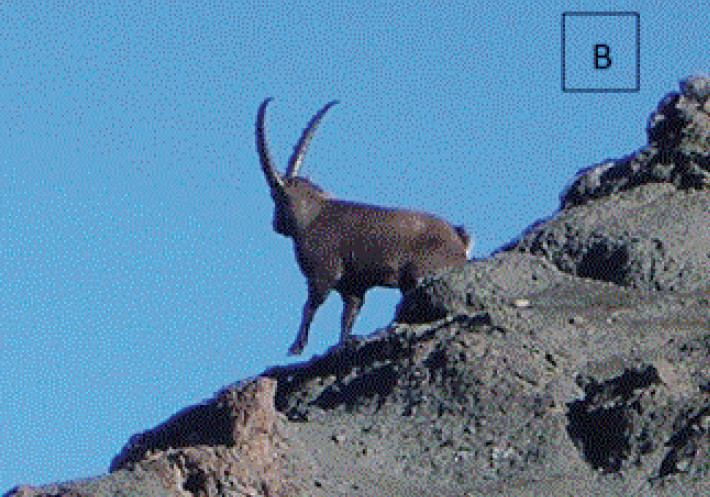
Alpine ibex goat (Capra ibex Linnaeus, 1758) in Argentina: a potential invasive species?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31687/SaremNMS24.10.5Keywords:
argentinian Patagonia, escape, geographical distributionAbstract
The ibex goat is a bovid of the Caprinae subfamily whose original distribution area encompasses the Alps mountain range. It occupies elevations between 1,600 and 3,200 m, living mainly above the forest line. It was introduced into Argentina in 1967, in the Parque Diana hunting reserve, located on the northern bank of Lake Meliquina (Lácar department, Neuquén). The presence of this species is
reported on the southern slope of Cerro Chapelco Grande and throughout the Chapelco range, and the potential for new translocations and its hybridization with domestic goats are discussed.
References
Ballari, S., M.N. Barrios-García, J. Sanguinetti, H. Pastore, & M. F. Cuevas. 2023. Hunting as a driver of mammal introductions. Introduced Invasive Mammals of Argentina (Valenzuela et al., eds.). SAREM, Serie A, Mammalogical Research, Buenos Aires.
Brambilla, A., A. Von Hardenberg, L. Nelli, & B. Bassano. 2020. Distribution, status, and recent population dynamics of Alpine ibex Capra ibex in Europe. Mammal Review 50(3): 267277. https://doi.org/10.1111/mam.12194.
Brambilla, A., N. Zehnder, B. Bassano, L. Rossi, & C. Grossen. 2024. Genetic evidence of a hybrid swarm between Alpine ibex (Capra ibex) and domestic goat (C. hircus). Evolutionary Applications 17:e13761. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.13761.
Cueto, M., M. R. Lanari, P. S. Bruno Galarraga, J. Fernández, & A. Gibbons. 2021. Caracterización reproductiva del caprino Criollo-Neuquino. Archivos Latinoamericanos de Producción Animal 29(34):199–221.
Chauveau, V., et al. 2024. Identifying the environmental drivers of corridors and predicting connectivity between seasonal ranges in multiple populations of Alpine ibex (Capra ibex) as tools for conserving migration. Diversity and Distributions 30:e13894. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.13894.
Chebez, J. C., & G. O. Rodríguez. 2014. La fauna gringa. Especies animales introducidas en la Argentina. 1ª edición. V. Mazzini y Fundación Félix de Azara, Buenos Aires.
Dupre, E., L. Pedrotti, & S. Arduino. 2001. Alpine Ibex Conservation Strategy. The Alpine ibex in the Italian Alps: status, potential distribution and management options for conservation and sustainable development. WWF International – Large Herbivore Initiative (Project 9E0154.01). <http://uagra.uninsubria.it/LHI/>.
Figueroa, C. E., et al. 2022. Patterns of genetic variation on wild pig (Sus scrofa) populations over a complete range of the species in Argentina. Mammalia 86:359–372. https://doi.org/10.1515/mammalia-2021-0141.
Gazzari, R. 1978. Fauna y caza en Neuquén. Siringa Libros, Buenos Aires.
Giacometti, M., R. Roganti, D. De Tann, N. Stahlberger-Saitbekova, & G. Obexer-Ruff. 2004. Alpine ibex Capra ibex ibex × domestic goat C. aegagrus domestica hybrids in a restricted area of southern Switzerland. Wildlife Biology 10:137–143. https://doi.org/10.2981/wlb.2004.018.
Guichón, L., M. Monteverde, L. Piudo, J. Sanguinetti, & S. Di Martino. 2016. Mamíferos introducidos en la provincia de Neuquén: estado actual y prioridades de manejo. Mastozoología Neotropical 23:255–265.
Houte De Lange, S. M. 1978. Zur Futterwhal des Alpensteinbockes. Zeitschrift für Jagdwissenschaft 24:113–138.
Iacolina, L., L. Corlatti, E. Buzan, T. Safner, & N. Šprem. 2018. Hybridisation in European ungulates: an overview of the current status, causes, and consequences. Mammal Review 49:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/mam.12140.
Moroni, B., A. Brambilla, L. Rossi, P. G. Meneguz, B. Bassano, & P. Tizzani. 2022. Hybridization between alpine ibex and domestic goat in the Alps: a sporadic and localized phenomenon? Animals 12:751–764. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12060751.
Parrini, F., J. W. Cain III, & P. R. Krausman. 2009. Capra ibex (Artiodactyla: Bovidae). Mammalian Species 830:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1644/830.1.
Relva, M. A., & Sanguinetti, J. 2016. Ecología, impacto y manejo del ciervo colorado (Cervus elaphus) en el noroeste de la Patagonia Argentina. Mastozoología Neotropical 23:221–238.
Signer, C., T. Ruf, & W. Arnold. 2011. Hypometabolism and basking: the strategies of Alpine ibex to endure harsh over-wintering conditions. Functional Ecology 25:537–547.
Tellarini, J. F., et al. Axis axis. Categorización 2019 de los Mamíferos de Argentina según su riesgo de extinción. Lista Roja de los mamíferos de Argentina (SAyDS–SAREM, eds.). <https://cma.sarem.org.ar>.
Toïgo, C., J. M. Gaillard, & J. Michallet. 1996. La taille des groupes: un bioindicateur de l'effectif des populations de bouquetin des Alpes (Capra ibex ibex)? Mammalia 60:463–472.
Toïgo, C., A. Brambilla, S. Grignolio, & L. Pedrotti. 2020. Capra ibex. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020:e.T42397A161916377. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T42397A161916377.en.
Vögel, C. A. 1969. Parque Diana. Paraíso para animales silvestres en la Argentina. Editorial Transilvana, Buenos Aires.

Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Bruno N. Carpinetti, Damián Peña, Salvador Vellido, Alexis R. Demartin, Celina Andreassi, Hernán Amendola, Mariano L. Merino

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.