Activity of the white-eared opossum Didelphis albiventris Lund, 1840, and its interaction with the yellow-crowned night heron Nyctanassa violacea (Linnaeus, 1758) in an urban mangrove in northeastern Brazil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31687/SaremNMS24.01.3Palabras clave:
behavior, biologic rhythm, marsupial, tideResumen
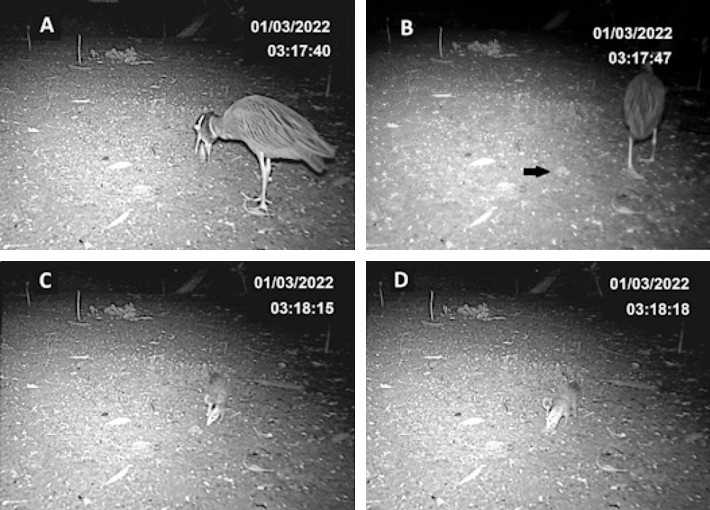
This paper shows, in time duration and frequency of records, the activity of the white-eared opossum Didelphis albiventris Lund, 1840, in a mangrove and its interaction with the yellow-crowned night heron Nyctanassa violacea (Linnaeus, 1758). We used six camera traps for ten months. Results from 596 recorded events showed a nocturnal circadian activity pattern. Events recorded show that the
opossum feeds on remains from the bird's predatory activity. The work discusses the behavior of taking advantage of resources involuntarily provided by other animals. It emphasizes the generalist and opportunistic characteristics of the opossum and its ability to adapt to different ecosystems.
Citas
Alessio, F., A. Mendes Pontes, & V. Silva . 2005. Feeding by Didelphis albiventris on tree gum in the northeastern Atlantic Forest of Brazil. Mastozoología Neotropical 12:53–56.
Bezerra-Santos, M. A., R. A. N. Ramos, A. K. Campos, F. Dantas-Torres, & D. Otranto. 2021. Didelphis spp. opossums and their parasites in the Americas: A One Health perspective. Parasitology Research 120:4091–4111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07072-4.
Cáceres, N. 2000. Population ecology and reproduction of white-eared opossum Didelphis albiventris (Mammalia, Marsupialia) in an urban environment of Brazil. Ciência e Cultura 52:171–174.
Cáceres, N. 2002. Food habits and seed dispersal by the white-eared opossum, Didelphis albiventris, in Southern Brazil. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment 37:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1076/snfe.37.2.97.8582.
Cáceres, N. 2003. Use of the space by the opossum Didelphis aurita Wied-Neuwied (Mammalia, Marsupialia) in a mixed forest fragment of southern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia 20:315–322.
Cáceres, N. C., & E. L. A. Monteiro-Filho. 2001. Food habits, home range and activity of Didelphis aurita (Mammalia, Marsupialia) in a forest fragment of Southern Brazil. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment 36:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1076/snfe.36.2.85.2138.
Calazans, J. F., & A. Bocchiglieri. 2020. Small mammals in restinga areas of north-eastern Brazil. Mastozoología Neotropical 27:298–305. https://doi.org/10.31687/saremMN.20.27.2.0.05.
Carvalho, F. M. V., P. S. Pinheiro, F. A. S. Fernandez, & J. L. Nessimian. 1999. Diet of small mammals in Atlantic Forest fragments in southeastern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Zoociências 1:91–101.
Cornelissen, G. 2014. Cosinor-based rhythmometry. Theoretical Biology and Medical Modelling 11:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742–4682-11-16.
Dias, C., & F. Perini. 2018. Biogeography and emergence of the genus Didelphis (Didelphimorphia, Mammalia). Zoologica Scripta 48:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1111/zsc.12306.
Eisenberg, J. F., & K. H. Redford. 1989. Mammals of the Neotropics. Vol. 1. 1st edition. University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Fernandes, M., F. Andrade, & J. Silva Júnior. 2006. Dieta de Micoureus demerarae (Thomas) (Mammalia, Didelphidae) associada às florestas contíguas de mangue e terra firme em Bragança, Pará, Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia 23:1087–1092. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81752006000400015.
Ferreira, M. S., & M. V. Vieira. 2014. Activity pattern of the Neotropical marsupial Didelphis aurita in south-eastern Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Journal of Tropical Ecology 30:169–172. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266467413000886.
Graipel, M., & M. Filho. 2006. Reprodução e dinâmica populacional de Didelphis aurita Wied-Neuwied (Mammalia: Didelphimorphia) em ambiente periurbano na Ilha de Santa Catarina, sul do Brasil. Biotemas 19:65–73.
Leite, Y. L. R., L. P. Costa, & J. R. Stallings. 1996. Diet and vertical space use of three sympatric opossums in a Brazilian Atlantic Forest reserve. Journal of Tropical Ecology 12:435–440. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266467400009640.
Lessa, L., R. Carvalho, & D. Astúa. 2023. Food habits of American marsupials. American and Australasian marsupials (N. C. Cáceres & C. R. Dickman, eds.). Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88800-8_22-2.
Marques, R., & M. Fabián. 2018. Daily activity patterns of medium and large neotropical mammals in an area of Atlantic rain forest at altitude. Revista Brasileira de Zoociências 19:38–64. https://doi.org/10.34019/2596-3325.2018.v19.24736.
Marsh, C., et al. 2022. Expert range maps of global mammal distributions harmonized to three taxonomic authorities. Journal of Biogeography 49:97–992. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.14330.
Nascimento, G., E. Ribeiro, & E. Moreira. 2020. Classificação climática da microrregião de Recife–PE. Geopauta 4:124.
Pereira Junior, R., R. Santana, R. Brito, & G. Rodrigues. 2019. Do manguezal à panela: aspectos bioecológicos da cadeia produtiva do guaiamum (Cardisoma guanhumi Latreille, 1825). Journal of Environmental Analysis and Progress 4:280–289. https://doi.org/10.24221/JEAP.4.4.2019.2735.280-289.
Periquito, M., G. Pereira, & M. Brito. 2008. Aves no manguezal do Espaço Ciência, Olinda, Pernambuco. Atualidades Ornitológicas 145:36–38.
Prevedello, J., R. Rodrigues, & E. Monteiro-Filho. 2009. Vertical use of space by the marsupial Micoureus paraguayanus (Didelphimorphia, Didelphidae) in the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. Acta Theriologica 54:259–266. https://doi.org/10.4098/j.at.0001-7051.063.2008.
Santiago, W., C. Fonseca, A. Zanzini, F. Machado, A. Moura, & M. Fontes. 2019. Activity pattern for medium and large mammals from the Cerrado domain. Natureza Online 17:16–25.
Santori, R. T., D. Astúa de Moraes, & R. Cerqueira. 1995. Diet composition of Metachirus nudicaudatus and Didelphis aurita (Marsupialia, Didelphoidea) in Southeastern Brazil. Mammalia 59. https://doi.org/10.1515/mamm.1995.59.4.511.
Silva, A. R., E. D. Forneck, S. A. D. L. Bordignon, & C. V. Cademartori. 2014. Diet of Didelphis albiventris Lund, 1840 (Didelphimorphia, Didelphidae) in two periurban areas in southern Brazil. Acta Scientiarum. Biological Sciences 36:241. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v36i2.20444.
Sollmann, R. 2018. A gentle introduction to camera-trap data analysis. African Journal of Ecology 56:740–749. https://doi.org/10.1111/aje.12557.
Srbek-Araujo, A., & A. Chiarello. 2013. Influence of camera-trap sampling design on mammal species capture rates and community structures in southeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 13:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1676-06032013000200005.
Yasuda, M. 2004. Monitoring diversity and abundance of mammals with camera traps: a case study on Mount Tsukuba, central Japan. Mammal Study 29:37–46. https://doi.org/10.3106/mammalstudy.29.37.

Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Leandro L. S. Nascimento, Maria G. B. Tenório, Fabiana C. Santana, Valdir L. Silva, Filipe M. Aléssio

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.